The Tesla logo is a badge that most of us instantly recognize, regardless of whether we’re well-informed about the car world or not. The American EV manufacturer has jumped to becoming the biggest-selling EV brand in the region and is the only company challenging the massive Chinese EV industry in its domestic and global markets. It has admittedly suffered from a sales decline in recent months, for several key reasons, but despite this, it continues to hold an impressive market share in the American new EV sales charts.

- Founded
-
2003
- Founder
-
Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning
- Headquarters
-
Austin, Texas, United States
- Current CEO
-
Elon Musk
- Status
-
Active
- Total Vehicles Sold In 2022
-
911,000
Despite its huge presence on American roads, there are a lot of us who may not be one hundred percent certain about what its iconic T-shaped badge actually means. Most car brands usually apply an insignia that bears a strong relevance to the company’s core philosophies and ethos. This is also the case with Tesla, as its unique badge has remained completely unchanged since its inception.
To give you the most up-to-date and accurate information possible, the data used to compile this article was sourced from Tesla and other authoritative sources, including Cox Automotive.
Tesla’s Clean And Unique Badge
The Symbol Of Its Rotor And Stator
The Tesla logo features a sleek, stylized T-like insignia that obviously represents the first letter of the company’s name, but its design carries a deeper meaning that is directly tied to its mechanical identity and engineering philosophy. Company founder and CEO Elon Musk highlights that the emblem depicts the cross-section of an electric motor. The central line represents one of the rotor poles, while the curved arc symbolizes a piece of the stator. This depiction directly links the badge to Tesla’s core technology, which was launched in 2003 when the company was founded.
RO Studio created the logo and has remained largely unchanged since it first graced the original Roadster. The decision to keep the same badging reinforces the brand’s already strong global recognition, while evolving in subtle refinements to match Tesla’s shift from niche EV start-up to global automotive disruptor. The badge’s minimalist black-and-white or silver-on-red presentation further complements Tesla’s futuristic and clean design ethos, which we get to see from both its interior and exterior.
A Design That Resonates Beyond Visual Elements
Some fans have speculated that the logo’s shape represents a shield or a cat’s nose, but it’s fully confirmed to signify an engineering connection. The badge’s relevance to the concentrated electric car portfolio lies in its visual encapsulation of the technology that powers them. It acts as a brand marker and a technical nod to the company’s motor design efficiency, high torque output, and energy optimization. In recent years, Tesla has expanded into battery technology, autonomous driving, and household energy products like Powerwall and Solar Roof. The logo’s clean and scientific feel is a consistent brand language that covers its automotive and energy fields. This ensures that its customers associate it with cutting-edge sustainability by embedding the essence of an electric motor into its brand identity.
Understanding Tesla’s Rotor And Stator Technology
The Components Of The Permanent-Magnet Motor
The permanent magnet synchronous motor is an important component in modern electric vehicles and is renowned for its efficiency and compact design. The rotor in these motors is embedded with permanent magnets that synchronize the rotor’s speed with the stator’s rotating magnetic field, ensuring that they rotate at the same frequency.
When an alternating current is supplied to an electric car’s stator, it generates a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnets in the rotor, creating a synchronous rotation that produces torque to drive the vehicle’s wheels. The synchronized rotation ensures optimal power conversion, maximizing efficiency and performance. The velocity of the vehicle is modulated by varying the frequency of the AC supplied to the motor. Advanced control systems in electric cars facilitate meticulous control over the motor’s operation, allowing for precise adjustments to speed and torque based on driving conditions, enhancing the vehicle’s adaptability and responsiveness.
A Versatile Power Source That Plays A Big Role
Synchronous permanent magnet motors are renowned for their high power density and efficiency, making them an optimal choice for electric cars where space and energy conservation are crucial. The utilization of permanent magnets eliminates the need for brushes, reducing wear and tear and maintenance needs, adding to the motor’s longevity and reliability. These motors are commonly used on the rear axles of Tesla EVs.
The synchronous permanent magnet motor harmoniously integrates compactness, efficiency, and precision control, propelling electric vehicles with optimal energy conversion and minimal loss. It stands as a testament to technological advancements in electric motor design, providing a balanced and sustainable propulsion solution in the evolving landscape of electric mobility, and reinforcing the pursuit of eco-friendly and high-performance transportation alternatives.
How Tesla Came To Be A Major Player
The Brand Was Very Different Before Musk’s Involvement
Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning are the two original engineers who founded Tesla Motors in 2003. Their goal was to create a series of electric cars that would completely dethrone gasoline as a preferred fueling method. Nikolai Tesla inspired the name because of their initial affinity for the AC motor technology, which some of its cars still feature. Eberhard and Tarpenning sought out major investors to make their dream a reality. Elon Musk, who had recently co-founded and sold PayPal during this time, was the most noteworthy investor, who allocated $6.5 million worth of Series A funding alone.
He was subsequently appointed the chairman of Tesla’s board of directors, bringing with him an infamous and ambitious vision for sustainable energy, electric vehicles, and power supply. Musk brought the strategic direction that Tesla needed to push the company toward high-performance electric vehicles. Eberhard and Tarpenning were initially in charge of the company’s day-to-day operations before departing in 2007. Musk then became the CEO in 2008, during which time the company struggled with financial stagnation.
Disrupting The Status Quo With A True Performer
The first Tesla Roadster was developed from 2004 to 2008 and marked a significant milestone in the entire electric vehicle industry. With this trend-setting alternative product, Tesla showed the world that electric cars can be fast, stylish, highly exclusive, and aspirational.
The designers and engineers built this new-age roadster on the already accomplished Lotus Elise chassis. They fit the compact layout with a custom-designed electric powertrain that offers drivers a good balance of performance and efficiency. This was also one of the first cars to feature a lithium-ion battery pack, which resulted in it being able to achieve an EPA-estimated 200-mile range between charges.
Tesla’s Disappointing Q2 2025 Sales Figures
The Latest Round Of Deliveries Was A Bit Lower Than Usual
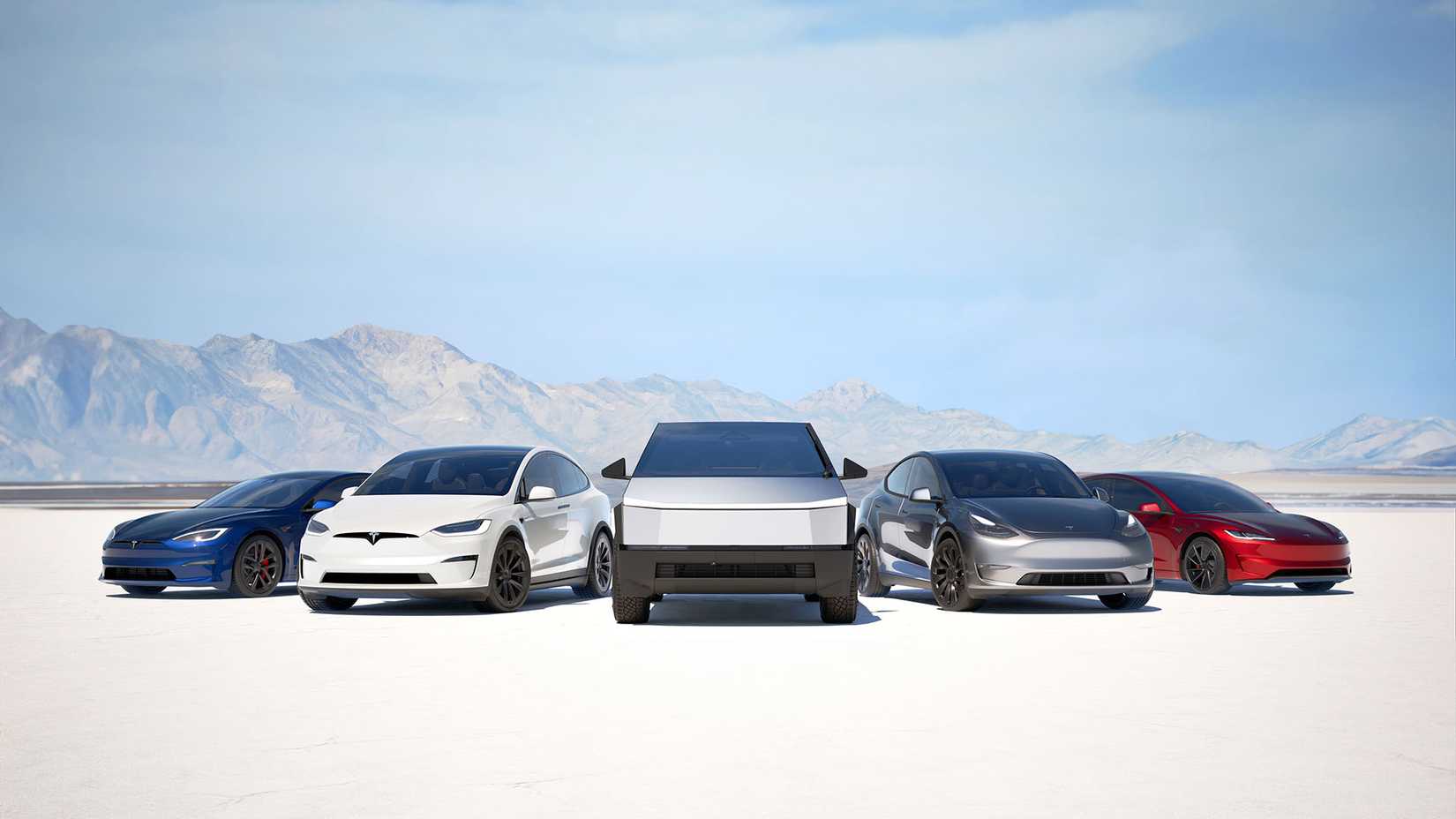
According to the Q2 2025 results, Tesla has suffered from a dramatic sales decline across the global market, with the U.S. being one of the most affected regions. According to Cox Automotive’s Q2 2025 EV sales report, Tesla suffered a 10.8-percent sales decline year-on-year. Bear in mind that the brand has still managed to sell 271,635 individual units across all five of its model lines this year so far, resulting in it holding a 46.2-percent market share. This is far more than any other manufacturer has been able to achieve and is likely a sales performance that no EV manufacturer will be able to match anytime soon.
Most Of The Roster Saw Declining Sales
The Tesla Model S suffers from the biggest sales decline this year so far, with the brand having only sold 2,715 copies, resulting in a 70.3-percent sales decline year-on-year. The Tesla Model X’s 44.9-percent sales decline is not as bad, but still poor, with the brand having sold a mere 6,714 copies. The Tesla Cybertruck suffers from a 7.3-percent sales decline, which we don’t think is too bad at all, given the level of controversy surrounding it. This year so far, the brand has delivered 10,712 copies.
The Tesla Model Y remains the brand’s biggest seller, with 150,171 copies sold, but this is still a 24.2-percent sales decline year-on-year. The Tesla Model 3 is the only vehicle in its catalog that benefits from a sales increase, which is as high as 37.8 percent, having sold 101,323 copies.